DAY 5: PREPOSITIONS & MODALS
IN/ON/AT (TIME & PLACE)
In English, we use different prepositions to talk about time & place:
TIME
To understand the GAP of using prepositions in English and Indonesian, let’s look at examples below:
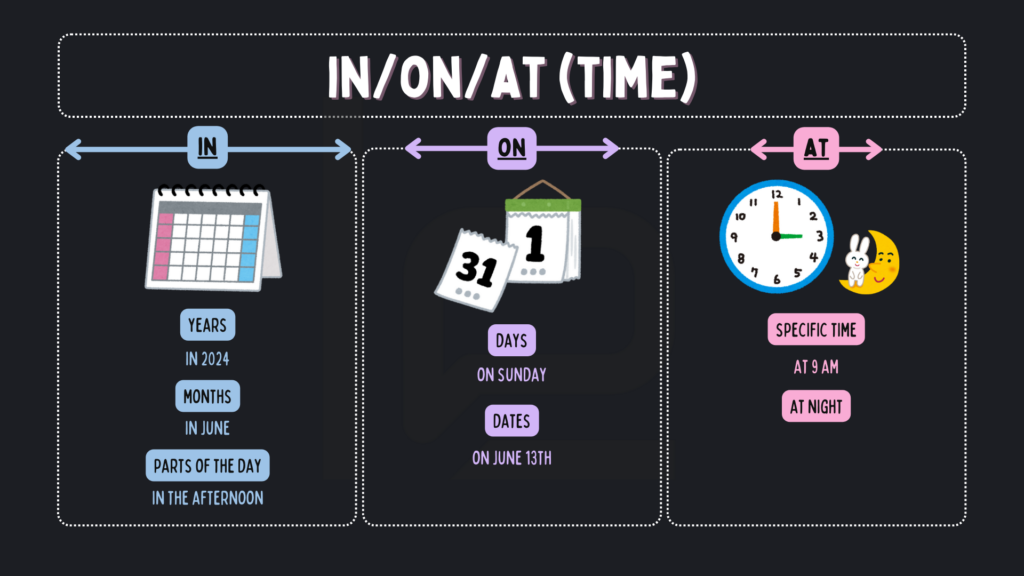
- Dia lahir pada tahun 2013. ➡️ He was born in 2013.
- Perayaan satu tahunnya jatuh pada tanggal 13 Juni 2020. ➡️ The anniversary is on June 13th, 2020.
- Mereka datang pada jam 9 malam. ➡️ They arrived at 9 PM.
As we can see, kita menggunakan preposisi yang berbeda di bahasa Inggris untuk sebuah kata yang sama, yaitu “pada”, di bahasa Indonesia. Cara menggunakan IN/ON/AT yang tepat untuk menunjukkan TIME adalah:
PLACE
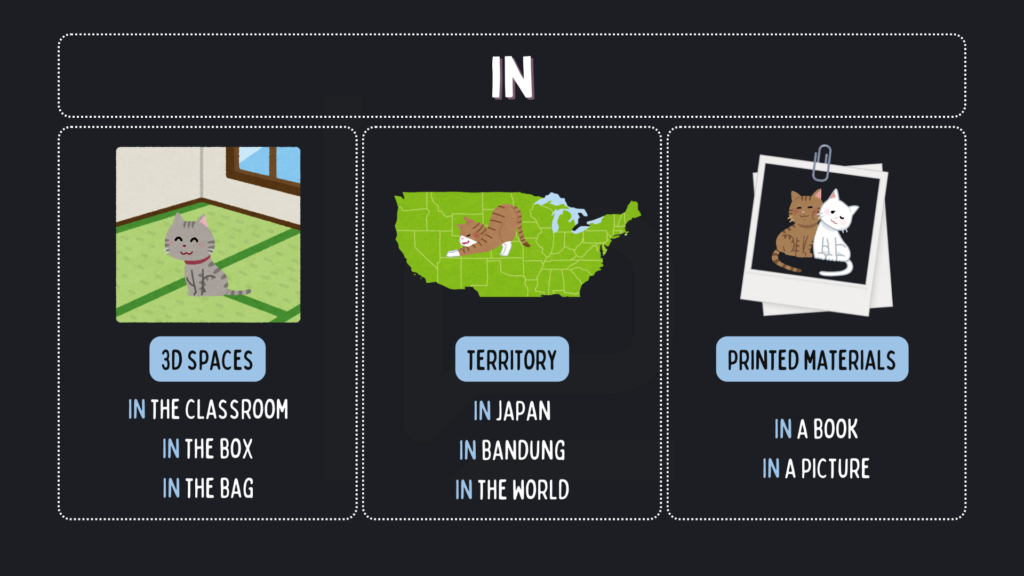
- Kuncimu ada di dalam tas. ➡️ Your key is in the bag
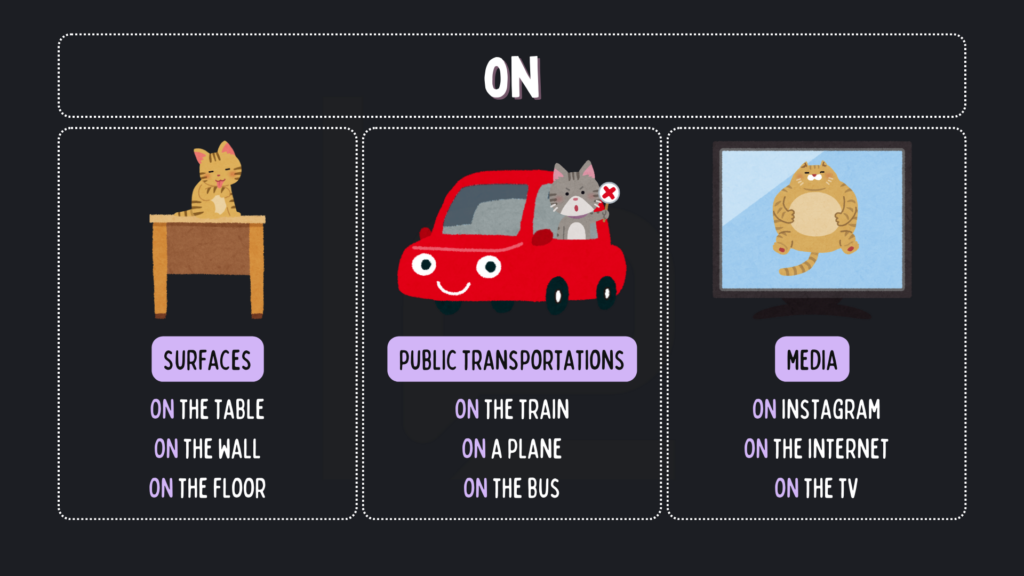
- Komputer berada di atas meja. ➡️ The computer is on the table
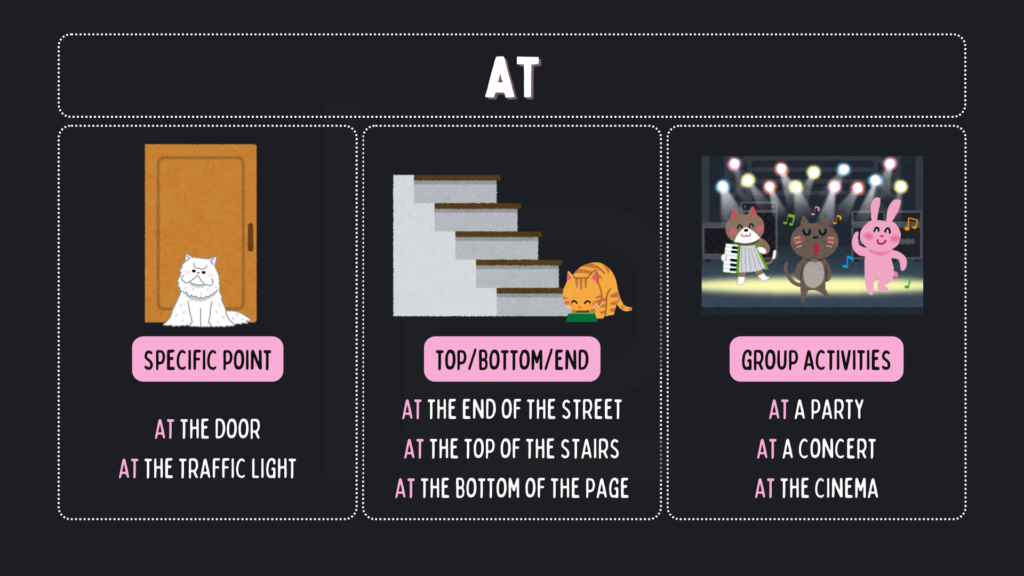
- Banyak baju kotor di sudut ruangan . ➡️ So many dirty clothes at the corner of the room.
Sama seperti sebelumnya, kita menggunakan preposisi yang berbeda di bahasa Inggris untuk sebuah kata yang sama, yaitu “di”, di bahasa Indonesia. Cara menggunakan IN/ON/AT yang tepat untuk menunjukkan PLACE adalah:
Those are the ways to use IN/ON/AT properly for TIME and PLACE in English. Let’s test your understanding using CHEAT SHEETS below:
INTRO TO HELPING VERB
Helping verbs “help” the main verb in a sentence by adding detail to the main verb. They always appear with ACTION VERBS. So far we have met DO/DOES
- We use forms of DO on PRESENT SIMPLE to:
- I do sleep at 8 every night. (Emphasis the positive sentences)
- I do not sleep at 8 every night. (Make negatives)
- Do you sleep at 8 every night? (Make questions)
- Remember that we use DOES for SHE/HE/IT/SINGULARS:
- My baby sleeps at 8 every night.
- My baby does sleep at 8 every night. (Emphasis)
- My baby does not sleep at 8 every night. (Negative, we don’t add ‘-s’ after the MAIN VERB “sleep”)
- Does your baby sleep at 8 every night? (Question, we don’t add ‘-s’ after the MAIN VERB “sleep”)
HELPING VERBS 2: MODALS
MODALS are helping verbs that show possibility, ability, suggestion, necessity, or permission. Here are some examples:
CAN (ABILITY)
We use “CAN” to talk about:
ABITILY
- Used to express someone’s ability to do something.
- Example: He can play the guitar.
POSSIBILITY
- Used to talk about something that is possible.
- Example: You can see the mountains from here.
PERMISSION
- Used to ask for or give permission.
- Example: Can I use your phone?
MUST (OBLIGATION)
We use “MUST” to talk about:
NECESSITY OR OBLIGATION
- Used to express something that is necessary or obligatory.
- Example: You must wear a seatbelt while driving.
STRONG RECOMMENDATION
- Used to strongly recommend something.
- Example: This movie is fantastic; you must see it!
SHOULD (ADVICE)
We use “SHOULD” to talk about:
ADVICE
- Used to give advice or make suggestions.
- Example: You should eat more fruits and vegetables.
EXPECTATION
- Used to express something that is expected or likely.
- Example: The train should arrive at 10 AM.
MIGHT (POSSIBILITY)
We use “MIGHT” to talk about:
POSSIBILITY
- Used to express a lower probability or possibility. It indicates that something is possible but not certain.
- Example: It might rain later, so take an umbrella just in case.
PATTERN
Semua MODAL VERBS hanya memiliki satu versi dan tidak akan berubah siapapun subjeknya. Yang perlu kita perhatikan adalah VERBS yang kita gunakan setelah MODAL VERBS haruslah VERB 1:
- I should to go there soon. ❌
- I should go there soon. ✅
- She should goes there soon. ❌
- She should go there soon. ✅
Mastering MODAL VERBS can improve your overall fluency significantly. Happy learning, Gems!